Access Affordability, and Outcomes

Download the Report
The health care sector plays a crucial role in the everyday lives of millions of Americans, yet many are left puzzled about how it all works. One key player in this complex system is managed care pharmacy, which operates largely behind the scenes but significantly shapes our access to and affordability of prescription medications. Curious to uncover the intricacies of how this vital component functions? Let’s dive in and explore the transformative impact it has on your health care experience!
In its third year, AMCP's annual Access, Affordability, and Outcomes report looks at the fundamental concepts of managed care pharmacy and provides insight and clarity into how today's changing health care climate can be navigated to improve patient care and outcomes. It discusses key areas of focus such as:
- The current state of prescription spending.
- Key statistics on health insurance and prescription drug coverage.
- Prescription utilization and out-of-pocket spending.
- Managed care pharmacy tools and their impact.
- Pharmacy types and pharmacy networks.
Download the Report (AMCP Members-only)
Introduction
The health care sector touches the daily lives of millions of Americans. However, there is often confusion or a lack of understanding about why it operates the way it does. Managed care pharmacy — often working behind the scenes but having a profound impact on access to and affordability of prescription medications — is not immune to this challenge. To address this, the Academy of Managed Care Pharmacy (AMCP) publishes this annual report to raise awareness of the existence, prevalence, and importance of managed care pharmacy in the lives of millions of Americans.
If you’re looking to better understand the fundamental concepts of managed care pharmacy, this report provides clarity. This report explores how professionals in this field work diligently to facilitate appropriate access to prescription treatments while remaining mindful of rising costs. It discusses key areas of focus such as:
- Pharmacy benefit design and implementation.
- Formulary and medication utilization management.
- Clinical programs.
- Quality and safety program management.
- Promoting affordability.
The report also highlights the most widely used managed care pharmacy tools: prior authorization, drug utilization, medication therapy management, and formulary design and management.
This report goes beyond the basics, offering a deep dive into the challenges facing managed care pharmacy and the opportunities it creates. Throughout the following pages, you’ll find extensive data-driven insights and studies — just as our professionals do daily.
The result is a comprehensive resource that makes a persuasive and detailed case about the value of managed care pharmacy. In a world with a pressing need for affordable access to necessary prescription medications, millions of Americans are looking for balanced solutions. Managed care pharmacy plays a crucial role — and this report demonstrates how.

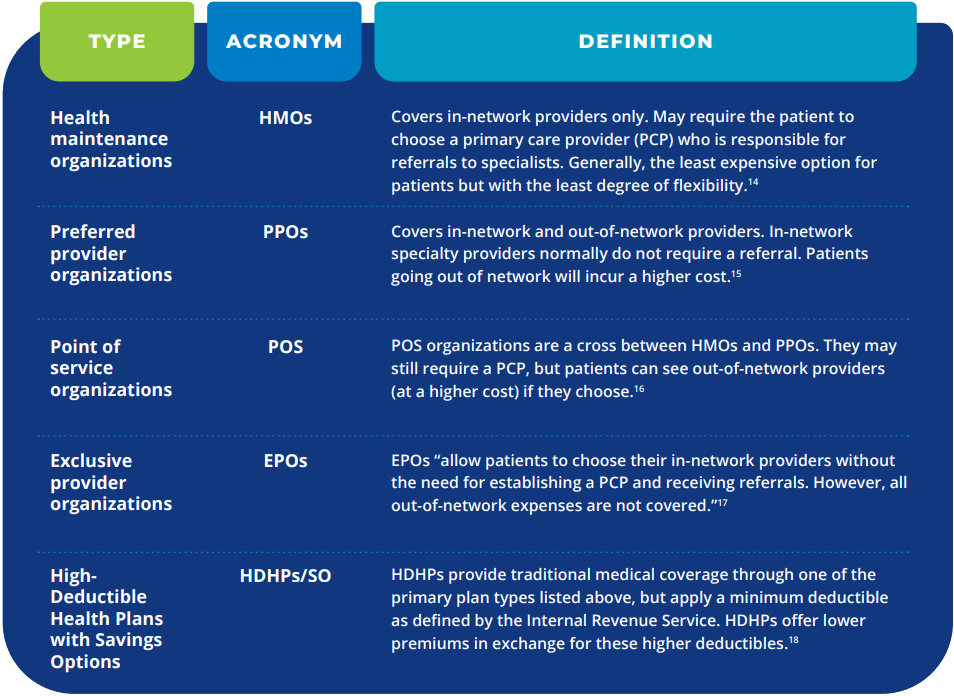
Table 1. Managed Care Plans
Managed care has evolved significantly since the first “prepaid health plan” and now encompasses four primary plan types in the commercial and employer market: health maintenance organizations (HMOs), preferred provider organizations (PPOs), point of service (POS) organizations, and exclusive provider organizations (EPOs).
Key Statistics
- U.S. prescription drug spending rose to $450 billion in 2023, a more than a tenfold increase since 1990, yet managed care pharmacy tools helped mitigate sharper cost growth.
- 85% of Medicaid beneficiaries and 54% of Medicare enrollees were covered under some form of managed care plan in 2023.
- Patients who gained insurance coverage filled 13–17% more prescriptions after coverage began, demonstrating the clear link between coverage and access.
- Medication adherence—a core measure of managed care effectiveness—was associated with reduced hospitalizations and improved outcomes across diseases including diabetes, cardiovascular conditions, and cancer.
- Specialty drugs and biosimilars continue to reshape the market: specialty drugs now account for nearly 50% of total drug spending, while biosimilars have driven competition and cost savings, with 72 FDA-approved products as of mid-2025.

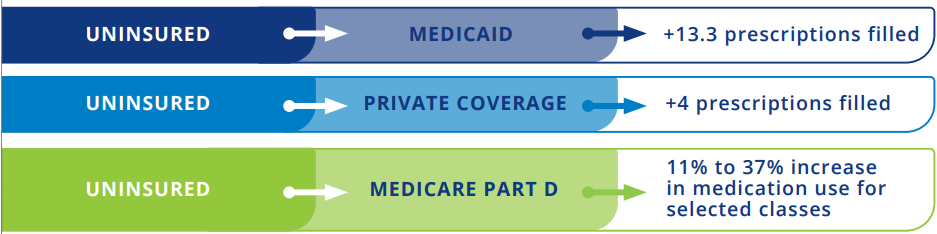
Figure 2: Impact of Gaining Insurance
Uninsured patients who gained insurance coverage filled a greater number of prescriptions after coverage began.
Conclusion
Managed care pharmacy tools play an important role in improving clinical outcomes, ensuring the appropriate use of medications, and containing rising costs. Through MTM and DUR, pharmacists can discover and help resolve medication-related issues or identify patients who would benefit from adding (or removing) certain medications from their drug regimens. Such interventions can help reduce adverse events or unnecessary hospitalizations, which are an undesired clinical outcome and a contributor to avoidable health care spending.
Prior authorization and step therapy seek to achieve evidence-based use of medications and to avoid unnecessarily costly medication when appropriate alternatives exist. Though opportunities exist to reduce the administrative burden of these protocols on clinical staff, these opportunities remain an important tool in containing rising drug spending. A well-designed formulary also plays a key role in providing patients with access to appropriate medications while encouraging utilization of cost-effective products. Likewise, development of pharmacy networks that balance access to conveniently located pharmacies while allowing health plans to reduce spending on prescription drugs is an important component of managed care pharmacy’s strategies to contain rising drug spending. Lastly, use of white/brown bagging and site of service policies can significantly reduce plan spending on specialty medications.
Prescription drug spending in the United States is forecasted to grow in the coming years. This growth will be driven by the emergence of innovative, potentially life-changing therapies, but many of those will come with a high cost. Managed care pharmacy’s role is to ensure those costs are reasonably contained while ensuring patients can access critical therapies. Managed care pharmacy tools play a key role in achieving the balance between access and cost.






